Abstract
Background:
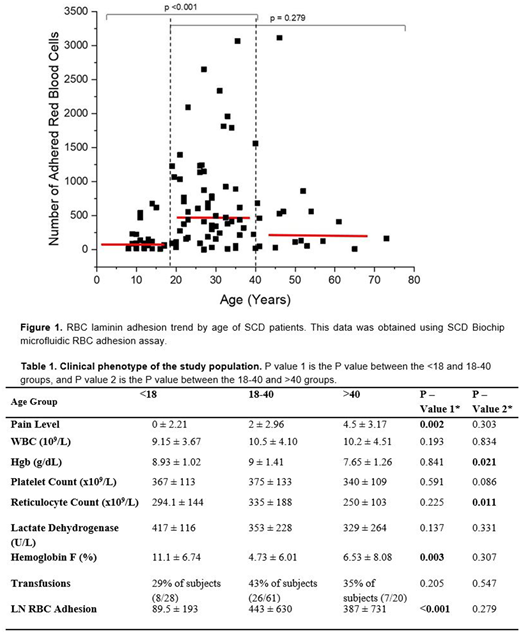
Sickle cell disease (SCD) is characterized by abnormal cellular adhesion to the endothelium, contributing to progressive vasculopathy and vaso-occlusion. The progression of the underlying pathophysiology in SCD with age is not well understood. We evaluated red blood cell (RBC) adhesion at clinical baseline to laminin (LN) in children and adults with HbSS, using the SCD Biochip.1 The SCD Biochip is a microfluidic device that recapitulates physiologic flow and allows quantitation of RBC adhesion to biological surfaces.1
Methods: This prospective cross-sectional study was conducted at The Children's Hospital at Montefiore in the Bronx, NY and University Hospitals Adult Sickle Cell Clinic in Cleveland, OH between 2014 and 2017. Blood samples were obtained from 29 children 8 to 18 years of age (33 samples, 28 HbSS and 1 HbSS HPFH (hereditary persistence of fetal hemoglobin), 13 males and 16 females), from 61 young adult patients 18 to 40 years of age (117 samples, 53 HbSS and 8 HbSS HPFH, 32 males and 29 females), and from 20 older adult patients >40 years of age (38 samples, 16 HbSS and 4 HbSS HPFH, 9 males and 11 females). All blood samples were obtained at clinical baseline. Of the children, young adult, and older adult populations, 45%, 46%, and 40% were on hydroxyurea treatment, respectively. Adhesion experiments were performed using surplus whole blood passed at physiological flow through LN-immobilized microchannels, and quantified after a wash step via microscope based on published protocols.1 Median values were used for multiple samples from a single individual.
Results:
Adults had higher, more heterogeneous RBC adhesion (440 ± 654, N=81) than did children (90 ± 193, N=29, not shown, p<0.001). Young adults tended to have higher adhesion than older adults (n.s.), as well as children (P<0.001, Figure 1). Young adults also had higher pain levels (relative to children, P=0.002) and higher reticulocyte counts (relative to older adults, Table 1, p=0.011), despite a higher total Hgb (P=0.012). As expected, children had a higher hemoglobin F level than young adults (Table 1, 11.1 ± 6.74 vs 4.85 ± 6.90, p=0.011).
Conclusions:
Our data demonstrates that adult patients with SCD have higher and more variable adhesion compared to pediatric patients with SCD, and this may be especially true in young adults. Older adults tended to have lower adhesion (perhaps due to compensatory genetic mutations that allowed them to survive before optimal pediatric care), but this was not statistically significant. Recall, as recently as the 1970s half of all Americans with SCD died before the age of 15 years of age. However, modern children with SCD are being treated aggressively with transfusions or hydroxyurea, and their low overall RBC adhesion reflects either these interventions or an innate low RBC adhesion during childhood. Increased adhesion in RBCs from young adults with SCD is congruent with increased mortality in the transition population2, and strongly suggests that modern treatments, as currently prescribed and taken, are insufficient to completely reverse the abnormal red cell physiology seen in young adults. Young adults have an increased RBC adhesion, possibly reflective of the natural history of SCD, and may benefit the most from anti-adhesive therapies and intensive interventions. Lower adhesion in children with SCD may also reflect an overall improved response to therapeutic interventions in children.
References:
Alapan Y, Kim C, Adhikari A, Gray KE, Gurkan-Cavusoglu E, Little JA, Gurkan. Transl Res. 2016 Jul;173:74-91.e8. doi: 10.1016/j.trsl.2016.03.008. Epub 2016 Mar 19.
Quinn CT, Rogers ZR, McCavit TL, Buchanan GR. Blood. 2010 Apr 29;115(17):3447-52.
Little:NHLBI: Research Funding; Doris Duke Charitable Foundations: Research Funding; PCORI: Research Funding; Hemex: Patents & Royalties: Patent, no honoraria.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal